anatomy of an innovation system
a framework designed to create and manage a lean innovation process within an organisation, focusing on the most essential elements needed to bring new ideas to fruition quickly and efficiently.
This work was part of the implementation of a global innovation strategy- designed, prototyped and validated with multiple regions and teams during 12 months. A white paper and innovation report was developed describing the full extent of our work and research, co-authored with the invaluable contributions of several others.
For inquiries about our work, reach out directly.
What is a system?
A set of things working together as parts of a mechanism or an interconnecting network; a complex whole
What is innovation?
The ability to generate and execute new ideas—incremental, evolutionary, or revolutionary— and its powered by creativity
A system of innovation is then…
Enablers: A way to understand what it takes for an idea to become a reality,
Ways of Working: A network of visible and hidden connections that push creativity forward,
Ambition: A strategy that acknowledges the big picture of complex challenges, including all important economic, social, political, organisational, institutional, and other factors that influence the development, diffusion, and use of innovations
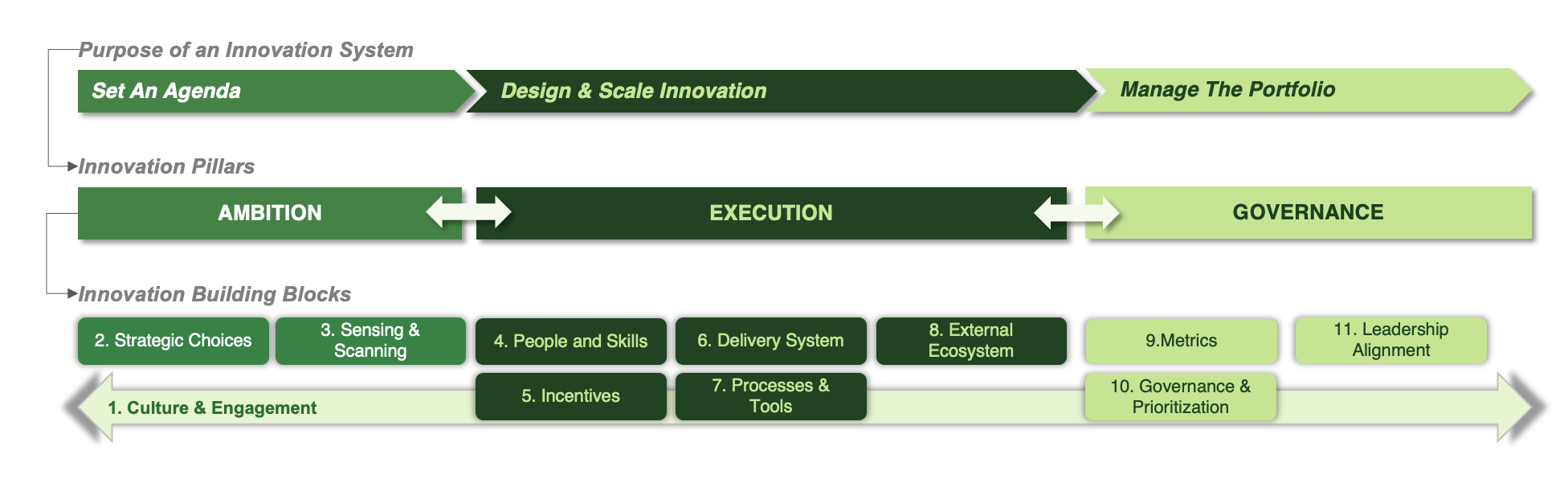
the building blocks of innovation
Our “Minimum Viable Innovation System” (MVIS) proposes an integrated approach to innovation:
Alignment behind a common Vision,
the right System to turn ideas-to-value
a foundational Portfolio for growth
Knowing there’s no silver bullet for innovation, we’ve learned that an innovation system is activated in three phases:
-
ALIGN INNOVATION VISION AND PORTFOLIO TO THE STRATEGY
Crystallise the role that innovation needs to play to deliver to the strategy and declare your strategic choices to build an innovation portfolio that will help hit your growth targets, balanced across different types of innovation, with different risk/reward profiles.
INVESTING IN CUSTOMER SENSING / HORIZON-SCANNING FOR 'PUSH' INNOVATION
Make deliberate investments and deploy the processes that will systematically scan the market and future trends, to constructively challenge the business on new opportunities and proactively capture ideas from customers and from emerging market opportunities.
-
HAVING CONSISTENT, AGILE WAYS OF WORKING THAT BRING TO LIFE WHAT 'GREAT' LOOKS LIKE
Facilitate cross-functional collaboration- between your local, regional, global, and corporate teams to develop new solutions/services/capabilities better and faster- integrating across regional, product and functional dimensions to capture, prioritise, incubate, and scale; sped up by an ecosystem of customers and partners
-
MORE GRANULAR, ACTIONABLE METRICS AND RUTHLESS PRIORITISATION
Across 'what' and 'how to take to market, continually tracking progress vs objectives; quickly pinpointing and learning from 'failure', using decision stage-gates and funding to surface what is and isn't meeting ambitions.
NURTURING AN INNOVATION CULTURE NEEDS DELIBERATE LEADERSHIP
Leaders across the entire organisation will have to navigate the change journey to get to the right mindset to execute at pace, across regions, categories and functions. Culture shifting is a deliberate call for leadership to embrace change and commit to it.
What makes an innovation system work?
-
Need for agility: Fast-paced market environments require rapid responses to emerging trends and disruptions
Resource constraints: Many organisations face limitations in funding, staffing or other resources
Technological advancements: New tech enables quicker, more efficient development and testing cycles
Cultural shift to experimentation: There is growing acceptance and encouragement of a fail-fast, learn-fast mentality in business
Pressure to innovate: Industry changing dynamics and innovative competitors drive the need for efficient systems to generate viable new products and services
-
Ad hoc availability: Important resources, including senior management, are called into the project without long preparation times
Cultural resistance: Some organizational cultures may resist the streamlined, risk-tolerant approaches MVIS requires
Lack of commitment: Senior leadership needs to understand and endorse the raw MVIS method to prevent it from faltering fast
Balancing core and new ventures: Allocating resources between maintaining core business operations and pursuing innovations can be challenging
Measuring impact: Establishing effective metrics to assess the success and ROI of MVIS initiatives can be complex
-
Secure executive sponsorship: Gain and maintain ad hoc support from top management to ensure the viability and resource allocation for MVIS
Overcome culture: Evangelise the MVIS to reduce cultural resistance within the organisation
Dynamic funding: Use venture capital (VC) tactics to support MVIS mindset, such as key risk mitigations as stage gates or setting funding thresholds to speed up the process
Define clear metrics: Establish what success looks like in the early stages and how it will be measured
Create a supportive environment: Encourage a mindset of experimentation and acceptance of failure as part of the innovation process
Tailor the system to organisational needs: Adapt the MVIS framework to fit the organization’s specific context and capabilities